Deploying an app on Kubernetes!

Deploying with an image
kubectl create deployment nginx --image nginx
We can verify the deployment we have just performed
kubectl get pods
The problem we will encounter when deploying in this way is that we do not have a way to get traffic to our pod so we will have to deploy a service that will allow us to have the communication traffic to the pod.
kubectl expose deployment nginx --type=LoadBalancer --port 80
This will create a load balancer which will assign us an external ip on the port we have indicated.
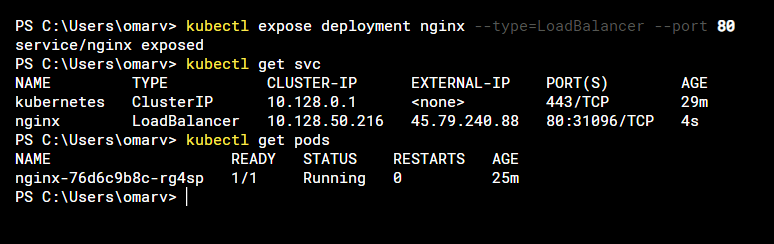
This way, in a rustic way, the deployment of our app from a container will be complete.
Deploying with a manifest
Create a YAML file
Create a YAML file that describes the resources you want to deploy to Kubernetes. You can use a text editor to create this file. Here is a basic example of a manifest file for a Deployment:
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: miapp
spec:
replicas: 3
selector:
matchLabels:
app: miapp
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: miapp
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
In this example, we are creating a Deployment called "miapp" with 3 replicas. We are using an image called "nginx:latest" and exposing port 8080.
Apply the manifest
Once you have created the manifest file, you can apply it using the kubectl apply command. Make sure you are in the correct directory where the manifest file is located and run the following command:
kubectl apply -f my-manifesto.yaml
This will send the manifest file to Kubernetes, which will create the resources specified in the file.
Verify deployment
You can check the deployment status using the kubectl command to get information about the deployed resources. Some useful commands are:
kubectl get deployments
shows the status of the deployments.
kubectl get pods
muestra el estado de los pods desplegados.
kubectl describe deployment miapp
displays detailed information about the "myapp" deployment.
If you need to make changes to your application, you can update the manifest file and apply the changes again using the kubectl apply command. Kubernetes will take care of the updates properly.